Index
I. What is One-Time Pin or One-Time Password (OTP)?
II. Types of OTP
III. OTP Implementation
IV. Common reason when & why to use OTP
V. Best Practices for OTP Implementation
VI. Challenges and Limitations of OTP
VII. Future Trends in OTP
VIII. Conclusion
What is One-Time Pin or One-Time Password (OTP)?

What is One-Time Pin (OTP)? Also referred to as One-Time Password, have emerged as a critical security measure in today’s digital landscape. OTPs provide an additional layer of authentication by generating a unique and time-limited code for each login attempt, effectively mitigating security risks. Whether used for online accounts, financial transactions, or physical access control systems, OTPs play a vital role in safeguarding against unauthorized access and fraudulent activities. After reading this article you will get all your answers attached to a question “What is One-Time Pin (OTP)”.
With the increasing prevalence of data breaches and identity theft, implementing robust authentication measures has become crucial. OTPs assist as a powerful tool in enhancing security by requiring users to enter a temporary code alongside their login credentials. This extra layer of verification poses a significant challenge for attackers attempting to replicate the code, thereby bolstering overall security.
In addition to protecting online accounts and financial transactions, OTPs find application in physical access control systems. Organizations utilize OTPs to secure physical entry points, such as buildings, rooms, or restricted areas. By requiring the correct OTP, only authorized individuals can gain access, ensuring the integrity and security of physical premises.
This article explores the implementation, best practices, challenges, and future trends of OTP. We will delve into its usage across online accounts, financial transactions, and physical access control. Furthermore, we will discuss the benefits of OTP, considerations for selecting the right solution, and troubleshooting common issues. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the importance of OTP in safeguarding both digital and physical access.
Types of OTP
OTP (One-Time Pin or Password) authentication offers different methods for generating unique and time-limited codes. These methods include Time-based OTP (TOTP) and Event-based OTP (HOTP). Understanding the characteristics, algorithms, and pros and cons of each type can help in selecting the most suitable OTP solution for specific needs.
A. What is Time-based OTP (TOTP)? A TOTP operates based on a time-synchronized algorithm. It generates unique passwords that are valid for a specific duration, typically 30 seconds. The TOTP algorithm combines a shared secret, usually stored on the user’s device and the current time, to generate the OTP. This ensures that the generated OTPs are valid only within the defined time frame.
The pros of TOTP include its simplicity and compatibility with various devices and platforms. It can be easily integrated into authenticator apps or security tokens, providing a convenient and portable OTP solution. However, TOTP requires accurate time synchronization between the device generating the OTP and the server validating it. In cases of time discrepancies, OTPs may become invalid, leading to authentication failures.
B. What is Event-based OTP (HOTP)? HOTP is based on a counter-based algorithm. Instead of relying on time synchronization, it generates OTPs based on a moving counter value. Each time a user authenticates, the counter increases, and a new OTP is generated. The server and the user’s device must remain in sync regarding the counter value to ensure OTP validity.
One advantage of HOTP is its independence from time synchronization, making it suitable for environments where accurate timekeeping is challenging. HOTP is less prone to time-related issues and can be used offline without relying on network connectivity. However, managing the counter value between the server and the device can be more complex, and the OTPs can become out of sync if the counter is not properly synchronized.
By understanding the characteristics of TOTP and HOTP, organizations can make informed decisions about their OTP implementation. Considerations such as ease of use, compatibility, time synchronization, and counter management are crucial in choosing the most appropriate OTP solution.
OTP Implementation
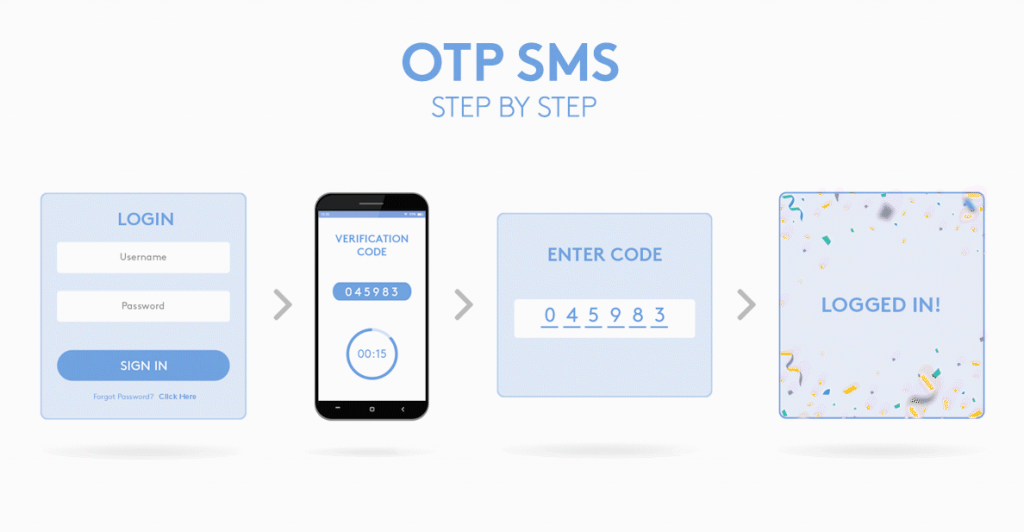
A. How to Generate OTP?
OTP generation is a critical aspect of implementing a secure authentication system. Generating OTPs involves creating unique and time-limited codes that provide an additional layer of security. The generation process typically relies on random or cryptographic algorithms to ensure the unpredictability of the OTPs.
When generating OTPs, two key considerations come into play: randomness and uniqueness. It is essential that the generated OTPs are truly random to prevent any patterns or predictability that could be exploited by attackers. Additionally, each OTP must be unique, ensuring that no two codes are the same to avoid any potential conflicts during the authentication process.
B. How to send OTPs?
After generating the OTPs, they need to be delivered to the intended recipients securely. Several methods are commonly used for OTP delivery:
- Text-based OTP: OTPs can be sent via text messages (SMS), WhatsApp, or other text-based messaging platforms to the user’s mobile device. This method is widely used and accessible, making it suitable for many scenarios. By leveraging the ubiquity of mobile phones and the convenience of text messaging, organizations can securely deliver OTPs to users for authentication purposes. Whether it’s through traditional SMS or popular messaging apps like WhatsApp, this text-based OTP delivery method ensures that users can receive their OTP codes directly on their mobile devices, enabling seamless and efficient authentication experiences.
- Email-based OTP: OTPs can be delivered through email, providing a convenient option for users who prefer receiving OTPs in their inbox. However, it is crucial to ensure the security of the email channel to prevent interception.
- Call-based OTP: In some cases, OTPs can be delivered through phone calls, where an automated voice system provides the code. This method is useful for users who may not have access to text messages or email.
- App-based OTP delivery: Authenticator apps, such as Google Authenticator or Authy, can generate OTPs directly on the user’s mobile device. These apps provide a secure and convenient way to receive OTPs, especially for services that support app-based authentication.
- Other delivery methods: Some organizations may utilize hardware tokens or smart cards to deliver OTPs. These physical devices generate and display OTPs, adding an extra layer of security. However, they require additional infrastructure and may be less commonly used.
In OTP implementation, selecting the appropriate OTP delivery method depends on factors such as user preferences, security requirements, and the platform or system being accessed.
What are some of the common reason to use OTP
The need for robust security measures has become paramount. Use of OTPs is one of the most frequently used method that addresses this concern. Let’s explore some common reasons why OTPs are widely adopted and how they enhance security in different cases.
A. Online Account Security
Protecting our online accounts from unauthorized access is crucial. OTPs play a vital role in bolstering security through a method known as two-factor authentication (2FA). By combining something the user knows (their regular password) with something they have (the time-limited OTP), online accounts become significantly more secure. Even if a malicious actor manages to obtain a user’s password, the additional layer of OTP verification acts as a strong deterrent.
Additionally, OTPs prove invaluable during password or account recovery processes. When users forget their passwords or need to regain access to their accounts, OTPs can be sent directly to their mobile devices through call or text or email to addresses. By successfully validating the OTP, users can recover their passwords or accounts, this confirms that only authorized individuals can regain access.
B. Transaction Authorization
When it comes to financial transactions and e-commerce purchases, trust and security are paramount. OTPs provide an effective solution for transaction authorization, adding an extra layer of security to mitigate fraud risks. Whether it’s transferring funds, conducting online banking activities, or making online purchases, users are required to input the OTP received through their preferred delivery method to validate and authorize the transaction. This validation process minimizes the chances of unauthorized transactions and safeguards user accounts and sensitive financial information.
C. Access Control
OTP technology extends beyond online accounts and financial transactions; it also plays a crucial role in access control scenarios. In physical access control systems, OTPs can be used to grant or deny entry to secure areas or facilities. By combining OTP verification with access cards or credentials, organizations can strengthen their overall access control mechanisms, ensuring that only authorized individuals with valid OTPs can gain entry.
For remote network access, OTPs serve as an essential tool to authenticate users connecting to secure networks or accessing sensitive data remotely. By requiring a valid OTP in addition to traditional login credentials, organizations can establish secure connections, preventing unauthorized access and protecting against potential data breaches.
In summary, OTPs offer a versatile and effective means of enhancing security across various scenarios. Whether it’s securing online accounts, authorizing transactions, or controlling access to physical and digital spaces, OTPs provide an additional layer of authentication that significantly strengthens security measures.
Best Practices for OTP Implementation
Implementing One-Time Pin (OTPs) requires careful consideration to ensure optimal security and user experience. By following best practices, organizations can enhance the effectiveness of OTP systems and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Let’s explore some key best practices for OTP implementation:
A. Length and Complexity of OTPs
The length and complexity of OTPs play a crucial role in their security. Longer OTPs with a mix of alphanumeric characters and symbols provide greater resistance against brute-force attacks. It is recommended to use OTPs with a sufficient length, typically consisting of at least six to eight characters, to ensure an adequate level of complexity.
B. Expiry Time and Renewal Frequency
Setting appropriate expiry times for OTPs is essential to balance security and usability. OTPs should have a limited lifespan to prevent their misuse in case of interception or theft. It is advisable to use shorter expiry times, such as a few minutes, to minimize the window of opportunity for attackers. Additionally, enforcing regular renewal of OTPs adds an extra layer of security by ensuring that compromised or expired OTPs become ineffective.
C. Protection against OTP Replay Attacks
OTP replay attacks involve intercepting and reusing OTPs to gain unauthorized access. To mitigate this risk, OTP systems should implement countermeasures to detect and prevent OTP reuse. Techniques such as one-time use flags or server-side validation can help protect against replay attacks, ensuring that each OTP can be used only once within a specified time frame.
D. Backup and Recovery Mechanisms
In situations where users may lose their mobile devices or encounter issues with their primary OTP delivery method, having backup and recovery mechanisms in place is crucial. Organizations should offer alternative OTP delivery channels, such as email-based OTPs or authenticator apps, to ensure users can regain access to their accounts even if their primary device is unavailable. Implementing secure account recovery processes helps users retrieve their OTPs and regain access to their accounts while maintaining appropriate security measures.
E. User Education and Awareness
User education and awareness are key to successful OTP implementation. Organizations should provide clear instructions and resources to educate users on how to set up and use OTPs effectively. It is important to emphasize the importance of keeping OTPs confidential, avoiding sharing OTPs with anyone, and being vigilant against phishing attempts or social engineering attacks. Regularly updating users on best practices and potential threats helps foster a security-conscious culture and minimizes the risk of OTP misuse.
F. Cost Considerations and Deployment Challenges
While OTPs provide enhanced security, organizations should consider the associated costs and deployment challenges. Factors such as infrastructure requirements, scalability, and user support must be taken into account when choosing an OTP solution. Organizations should evaluate different options, considering factors such as hardware tokens, authenticator apps, or SMS-based OTP delivery, and select a solution that aligns with their budget, operational requirements, and user base.
By following these best practices, organizations can optimize OTP implementation and ensure a robust and secure authentication mechanism.
Challenges and Limitations of OTP
While One-Time Passwords (OTPs) provide an additional layer of security, they are not without their challenges and limitations. It is important to be aware of these potential vulnerabilities and trade-offs when implementing OTP as an authentication method. Let’s explore some of the key challenges and limitations of OTP:
A. Potential Vulnerabilities and Attacks
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: OTPs can be susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker intercepts communication between the user and the authentication server. In such attacks, the attacker can obtain the OTP and impersonate the user to gain unauthorized access. Implementing secure communication protocols, such as HTTPS, and using additional security measures like mutual authentication can help mitigate this risk.
- OTP Replay Attacks: OTP replay attacks involve intercepting and reusing OTPs to gain unauthorized access. Attackers may capture OTPs during transmission and use them at a later time to impersonate the user. Implementing measures like one-time use flags, server-side validation, or time-based OTPs can help prevent OTP replay attacks and ensure that each OTP remains valid for a limited time.
B. User Experience and Convenience Trade-Offs
OTP authentication can introduce certain trade-offs in terms of user experience and convenience:
- Time and Effort: OTP authentication requires users to enter a new password each time they authenticate, which can be time-consuming and potentially frustrating, especially in situations where frequent authentication is required.
- Dependency on Devices: OTPs typically rely on users having access to their mobile devices or other OTP delivery methods. In cases where users forget their devices or experience technical issues, they may face challenges in accessing their accounts.
- User Education and Adoption: Implementing OTP authentication may require user education and training to ensure proper understanding and usage. Some users may find it unfamiliar or confusing initially, requiring clear instructions and support to facilitate adoption.
- Dependency on Connectivity: OTP delivery methods like SMS or app-based OTPs rely on network connectivity. In areas with weak or no network coverage, users may face difficulties receiving OTPs, affecting their ability to authenticate.
Despite these challenges and trade-offs, OTPs remain a widely used and effective authentication method, providing an additional layer of security for various applications.
Future Trends in OTP
As technology continues to advance, the landscape of One-Time Pins (OTPs) is evolving to enhance security and user experience. Let’s explore some of the future trends that are shaping the realm of OTP authentication:
A. Biometric-based OTP Authentication
Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or iris scanning, is gaining traction as a secure and convenient method for user verification. In the future, we can expect the integration of biometric data with OTP authentication to provide an additional layer of identity verification. This combination offers stronger security by validating the user’s unique biometric features along with the dynamic OTP, ensuring a more robust authentication process.
B. Context-Aware OTP Mechanisms
Context-aware OTP mechanisms leverage contextual information, such as user location, device information, or behavioral patterns, to enhance the security of OTP authentication. By analyzing the context in which the authentication request is made, these mechanisms can identify anomalies or suspicious activities. For example, if a user typically accesses their account from a specific location and suddenly attempts to authenticate from a different country, the system can trigger additional verification steps or deny the authentication attempt. Context-aware OTP mechanisms add an extra layer of security by considering the broader context surrounding the authentication process.
C. Advancements in OTP Delivery Methods
The delivery methods of OTPs are also evolving to offer more seamless and user-friendly experiences. Push notifications, delivered through mobile apps or other connected devices, are becoming increasingly popular. With push notifications, users can receive OTPs directly on their devices without the need to switch between different applications or input codes manually. This streamlined approach enhances convenience while maintaining a high level of security.
Conclusion
In an increasingly digital world, the importance of One-Time Passwords (OTPs) in enhancing security cannot be overstated. Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of OTP implementation, its common applications, challenges, and future trends. Let’s recap the key points and reflect on the future of OTP.
OTP serves as a crucial component of authentication, providing an extra layer of security beyond traditional passwords. It is widely used for two-factor authentication, adding an additional verification step to ensure that only authorized users gain access to online accounts, financial transactions, e-commerce purchases, physical access control systems, and remote network access. By generating a unique password for each authentication attempt, OTP mitigates the risks of password breaches and unauthorized access.
Looking ahead, the future of OTP holds promising advancements. Biometric-based OTP authentication, integrating biometric data with OTPs, will enhance security by combining the uniqueness of an individual’s biometrics with dynamic passwords. Context-aware OTP mechanisms, leveraging contextual information, will detect anomalies and further strengthen the authentication process. Moreover, advancements in OTP delivery methods, such as push notifications, will offer seamless user experiences without compromising security.
At SyncTech, we understand the significance of OTP in safeguarding digital assets. Our OTP solution is designed to provide robust security measures while prioritizing user convenience. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and industry best practices, our solution ensures secure access to online accounts, financial transactions, and more. For detail of our solutions please visit www.synctechsol.com/otp.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, OTP remains a critical tool in combating cybersecurity threats. By implementing OTP and staying informed about the latest trends and best practices, individuals and organizations can enhance their security posture and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
